The Essential Role of Odorants in Gas Safety
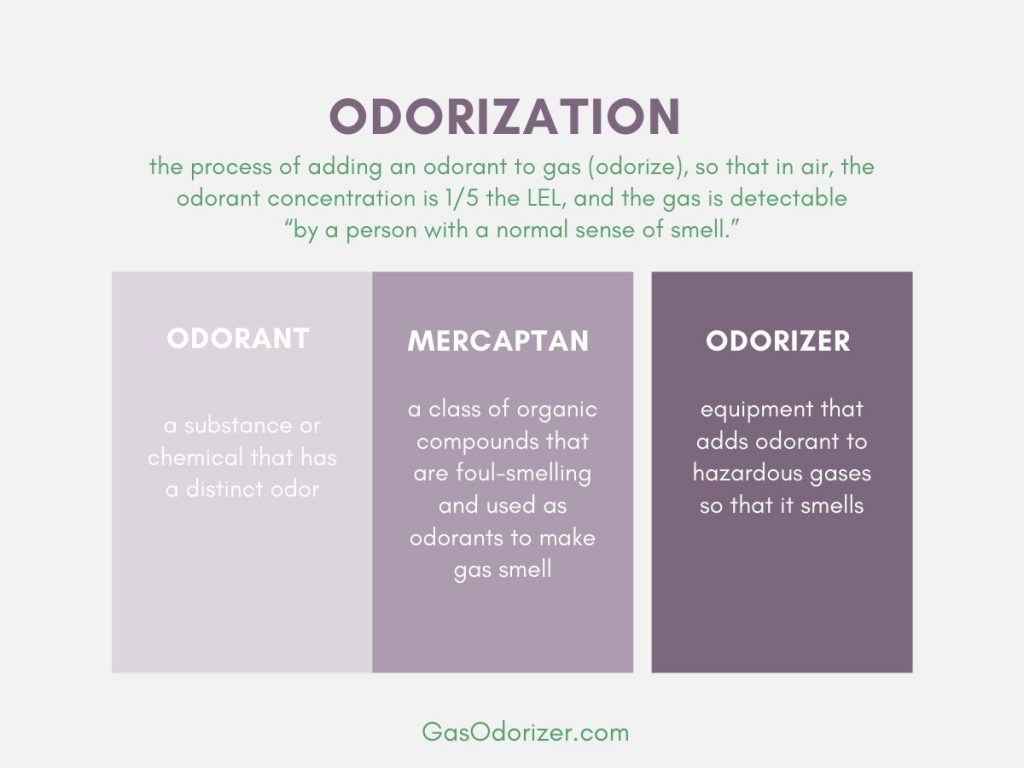
In its natural state, natural gas is primarily composed of methane and is colorless and odorless. This combination created serious safety concerns until the development of gas odorants. These specialized compounds, particularly mercaptan, transform odorless gas into an easily detectable substance, creating an essential gas leak detection system that protects communities.
How Gas Leak Detection Through Odorants Saves Lives
A tragic 1937 incident at a London, Texas school, where unscented gas led to an explosion claiming over 200 lives, demonstrated the critical need for reliable gas leak detection. This event transformed gas safety standards, leading to mandatory odorant requirements across Texas and eventually nationwide.
Current Gas Safety Standards
Today’s federal regulations require:
- All gas in distribution pipelines must contain detectable odorants
- The odorant must enable gas leak detection at 1/5 of the lower explosive limit
- Transmission lines in populated areas require odorant gas for safety
- Special safety monitoring maintains proper odorant levels
Understanding Odorants and Gas Safety Equipment
Common Gas Odorants
The distinctive smell in natural gas comes from carefully selected compounds:
- Mercaptans (providing the characteristic sulfur smell)
- Other specialized odorant blends for optimal gas leak detection
Safety Equipment for Odorant Addition
Various systems ensure proper mixing of odorants in natural gas:
- Injection systems for precise odorant control
- Equipment that monitors odorant levels
- Safety systems preventing over-odorization
Frequently Asked Questions About Gas Safety and Odorants
Q: Why does natural gas have a distinctive smell?
A: Natural gas is odorless in its natural state. Gas companies add odorants, typically mercaptans, creating a distinctive smell that enables quick detection of gas leaks.
Q: How do odorants improve gas safety?
A: Odorants serve as an early warning system. When someone smells the distinctive odorant, it alerts them that gas is present and it is time to act, which may be to evacuate and contact emergency services to prevent potential accidents.
Q: What creates the smell in natural gas?
A: The smell comes from added odorants, primarily mercaptan compounds, which give the gas its characteristic rotten egg odor – a crucial feature for gas leak detection.
Modern Gas Safety Solutions
Today’s gas safety technology combines traditional odorant use with advanced monitoring systems. GPL Odorizers leads in this field with equipment that ensures consistent odorant levels while protecting the environment.
Learn More About Gas Safety Solutions
-
[…] “What is Natural Gas Odorization?” we mention that natural gas by itself is odorless and because it is combustible an odorant is […]
Leave a Comment


Is there a different sent they use for natural gas and for propane I was under the impression Mar captain was for propane and Kurcaptain was for natural gas
Yes, they use different odorant formulation for propane gas and presumably butane gas. Forgot what it is.
Thank you for sharing this informative article about scent eliminator. I hope there are a lot of consumer who could read this and be guided accordingly.
Just because humans cannot detect natural gas with our olfactory bulbs does not mean it is odorless. It just means we cannot smell it.